3 User Workspace
3.1 Overview
The User Workspaces within the APEx Instantiation Services provide secure, personalised environments for individual users to perform a wide range of tasks including development, data processing, visualisation, and analysis. These single-user environments are managed by JupyterHub and dynamically provisioned using Kubernetes, ensuring scalability, isolation, and ease of use. Key features and capabilities of the User Workspaces include:
- Secure, Isolated Environments: Each user is provided with a dedicated namespace within the Kubernetes cluster, ensuring resource isolation and secure data management.
- Customizable Workspaces: Workspaces can be tailored to user needs with specific configurations and tools, including pre-configured environments for tasks like data analysis and machine learning.
- Seamless Integration with APEx Services: Integration with other APEx services such as the Interactive Development Environment (IDE) and Product Catalogue for enhanced functionality and data accessibility.
- Robust Data Management: Secure storage and retrieval of data using PersistentVolumeClaims (PVCs) and integration with external data sources
3.2 Showcase Scenarios
The User Workspaces support a variety of use cases, making them versatile tools for the EO community. Some typical scenarios include:
Development and Testing: Researchers and developers can use the User Workspaces to develop and test new algorithms and models. For instance, a user might leverage the IDE integrated with JupyterHub to write and debug Python scripts for processing satellite imagery.
Data Analysis and Visualization: Analysts can perform exploratory data analysis and create visualisations using tools like JupyterLab or QGIS. For example, an analyst might use Jupyter notebooks to analyse climate data and visualise trends over time.
Educational and Training Purposes: The User Workspaces can be used to create interactive tutorials and practical assignments that guide users through various aspects of APEx, from setting up workspaces and accessing data in the Product Catalogue to using the IDE for development tasks.
3.3 User stories
3.4 Business model
3.5 Technical Architecture
The User Workspaces are built on advanced technologies and frameworks to ensure robustness and scalability. JupyterHub provides a publicly accessible web interface for authenticated and authorised users to instantiate their Application Hub pod instances securely. KubeSpawner, a Kubernetes-native spawner for JupyterHub, dynamically creates and manages Jupyter Notebook servers within the Kubernetes cluster on server initiation.
When a user launches their server, several Kubernetes resources are created. Each user is allocated a dedicated namespace, providing a secure and organised virtual environment within the Kubernetes cluster. Configuration data is stored separately from the application’s code in a ConfigMap, which can include Conda environment configurations. PersistentVolumeClaims (PVCs) are created to request storage resources, specifying the necessary size and access modes for mounting volumes with read/write access. Finally, a pod is created and started using a dedicated profile based on the user’s selection.
A PostgreSQL database is used to store user information for JupyterHub, managing authentication and user data. Data management involves secure storage and retrieval facilitated through PVCs and integration with external data sources. Users can access and share data within the workspace efficiently.
Workspace setup and customization allow users to configure their environments with specific tools and configurations required for their tasks. Integration with other APEx services, such as the IDE for enhanced development capabilities or specialised Dashboards, further enhances the functionality of the User Workspaces. Security and compliance measures ensure that only authenticated users can access their workspaces, with data privacy and regulatory compliance measures in place to protect user data.
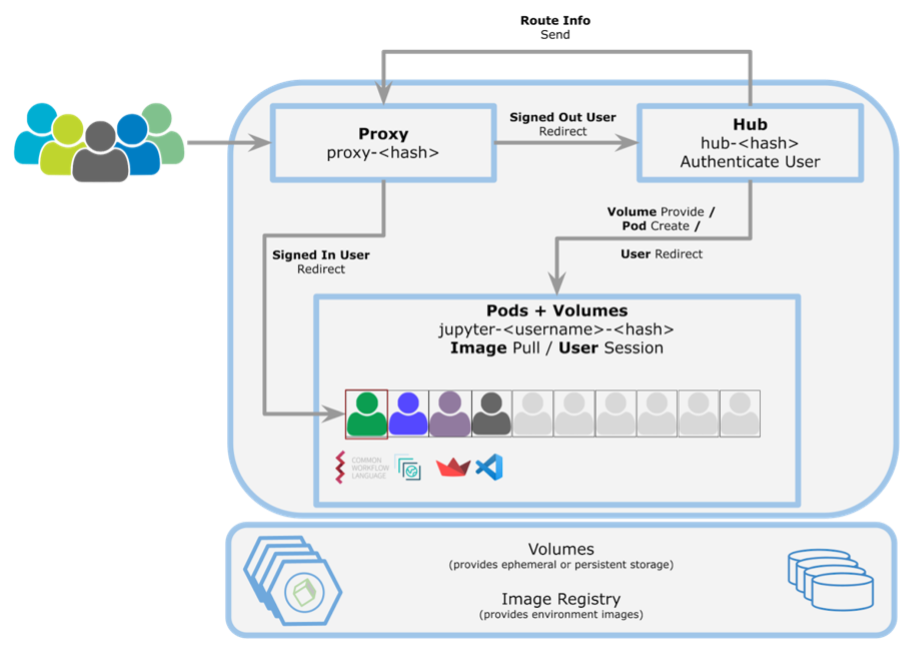
The diagram above illustrates how user sessions are created, authenticated, and managed within the Kubernetes infrastructure. It highlights the roles of the Proxy, Hub, pods, volumes, and Image Registry in providing secure, isolated, and customised environments for individual users. The system ensures efficient resource management and a seamless user experience for various tasks including development and data analysis.
3.6 Operational Management
Deployment and scaling of User Workspaces are managed by Kubernetes which handles the scaling of resources, allowing the platform to accommodate varying workloads and user demands efficiently. Continuous monitoring of the Kubernetes cluster and JupyterHub instances ensures optimal performance and availability. Automated maintenance tasks, such as updates and backups, minimise downtime and ensure data integrity, providing a robust and reliable environment for users.